Strategic Communication Architecture in Agentic AI Workflows: Why Channels Matter More Than Ever
In the age of intelligent agents and AI-driven automation, building custom workflows using tools like LangChain, LangGraph, and CrewAI has become increasingly feasible and powerful. These frameworks offer flexibility that pre-built workflow automation tools (like n8n or Zapier) often lack—particularly when we dive into complex architectures involving multiple agents, gateways, and distributed task workers.
However, with this power comes the need for precise orchestration and communication. When systems scale beyond a few interconnected nodes, communication strategy becomes the backbone of system stability, responsiveness, and scalability.
Why Communication Strategy is Crucial
Agentic systems today are more than just scripts chained together. They involve:
- Multi-agent collaboration for reasoning and decision-making
- Task workers running on separate nodes (sometimes asynchronously)
- Gateways handling various entry and exit points (e.g., webhooks, APIs, human feedback)
- Real-time interactions with users and data streams
In such setups, defining the right communication channel is as important as the workflow logic itself. The choice impacts latency, fault tolerance, observability, and system modularity.
Choosing the Right Communication Mechanism
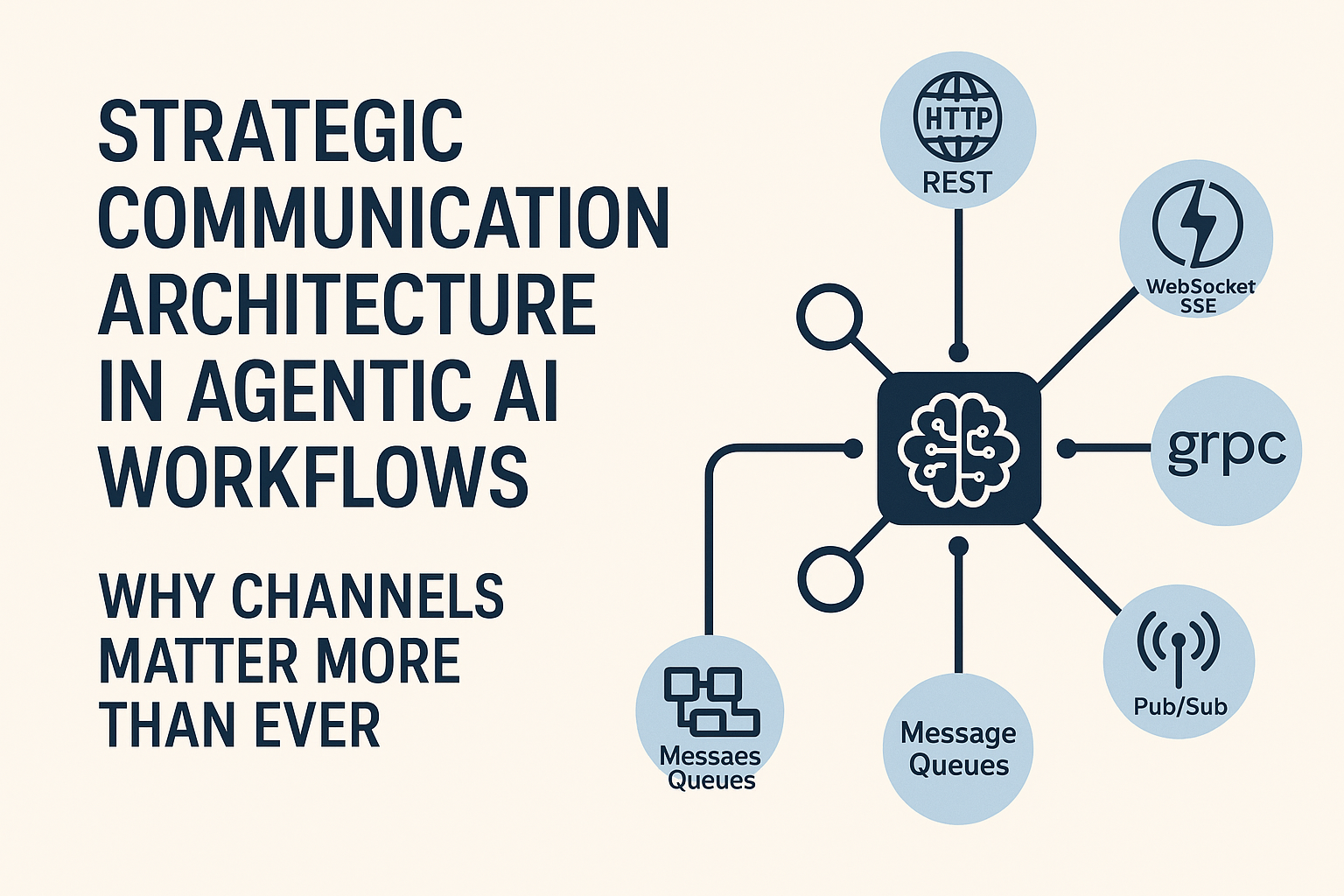
Here's a strategic breakdown of when to use which communication method:
| Channel | Best Use Case |
|---|---|
| HTTP/REST | Best for loosely coupled, stateless interactions. Ideal for external APIs or occasional inter-service calls. |
| WebSocket/SSE | Vital for real-time applications like dashboards or collaborative agents. They provide persistent, low-latency channels for streaming data. |
| gRPC | Great for internal microservices communication. Offers performance, bi-directional streaming, and strong typing—suitable for systems with heavy internal traffic. |
| Message Queues (Kafka, SQS, RabbitMQ) | Essential when dealing with asynchronous, decoupled task flows. Excellent for scaling workflows and handling retries or failures gracefully. |
| Pub/Sub Patterns | Use when events need to fan out to multiple listeners or when dealing with data pipelines. |
Best Practices
- Decouple agents and tasks using queues to prevent single points of failure and improve scalability.
- Use WebSockets or SSE for real-time human-in-the-loop scenarios, such as feedback or validation gateways.
- Adopt gRPC for internal high-performance service mesh communications, particularly when LangGraph nodes are deployed across services.
- Centralize observability—implement tracing (e.g., OpenTelemetry), logging, and monitoring across channels.
- Standardize message formats (JSON, Protobuf) to ensure compatibility and simplify debugging.
Final Thoughts
As agent-based systems evolve, so must our communication design strategy. Whether orchestrating AI agents across domains or integrating legacy systems into intelligent workflows, your channel architecture defines how well the system performs under pressure.
In short: the future of scalable, intelligent automation lies as much in how we connect as in what we connect. © 2025 KyszTech Pvt. Ltd. | kysz.tech
Comments (0)
No comments found.